Table of Contents
The widespread adoption of 5G technology is set to change the world in numerous ways. With unlimited data, faster speeds, and low latency, 5G is driving fundamental changes in consumer data usage behavior. In this blog, we will discuss the drivers for mass adoption of 5G, related CSP (Communication Service Provider) competition and the rising cyber-risk in the 5G world. Lastly, we will introduce how a Network Native Security solution is crucial in managing consumer cyber-risks & ensuring 5G’s continued proliferation.
5G-led Transformation
The transformative impact of 5G has been talked about for a while now, but what will the actual real-world impact of this technology be on the average consumer?
This is one of the fundamental questions in the minds of CSPs.
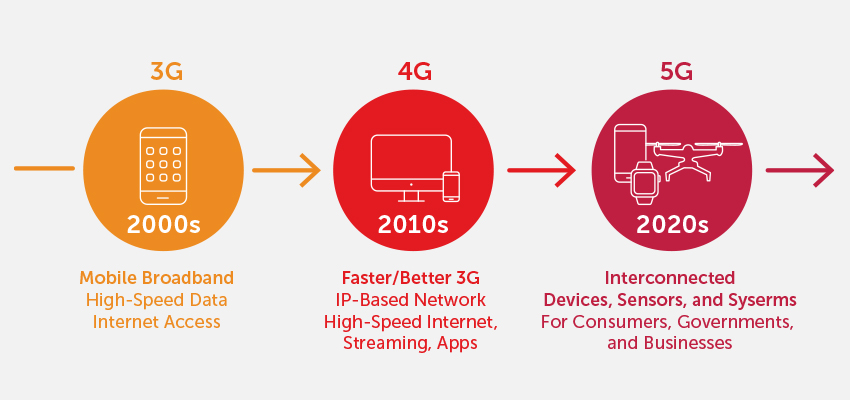
Looking back at previous shifts in mobile technology, 3G introduced multimedia for the first time, and 4G led to the rapid proliferation of mobile applications, video content streaming, and fully native mobile apps for on-the-go consumption. 4G transformed the smartphone into the center of our digital world. Now, 5G is unlocking the next big shift in mobile consumer applications and driving a fundamental change in consumer usage behavior. The promise of 5G is unlimited data with blazing fast speeds, extremely low latency, and exceptionally high throughput, enabling customers to use their mobile devices like never before.
Perhaps even more significant will be the explosion of machine-to-machine communication, as IoT devices leverage the above capabilities to accelerate the adoption of new services, powered by devices such as smart glasses, kits for tactile internet, medical sensors, and more. There will be an exponential increase in mobile traffic from all kinds of new devices, powering new applications that were not possible on 4G, thanks to a newly available ultra-low latency and high throughput. The impact of 5G will not just be limited to mobile consumer applications, 5G will also be the bedrock for IoT-driven services, including upcoming Web 3.0 and Metaverse applications.
With unlimited data and speeds measured in Gigabits per second, we anticipate a sea change in how consumers will use their devices and the fixed network. The question is why a consumer would choose to connect their 5G unlimited-data mobile device, via their home router, to a fixed network (where on average, over 25 different devices such as Laptops, Tablets, IoT devices, etc., are sharing the fixed network resources). What customers want is to have the best experience and to operate seamlessly between the two networks. While the fixed network would still be appropriate for devices that do not have wireless radio, most of the 5G-enabled devices would make wireless networks their primary network of choice. This is especially true for 5G unlimited plans, where customers get dedicated speeds and can leverage the power of low latency and network slicing to get a better quality of experience.
5G Security Risks
As the industry moves toward mass 5G adoption, managing cyber risks will be more important than ever.
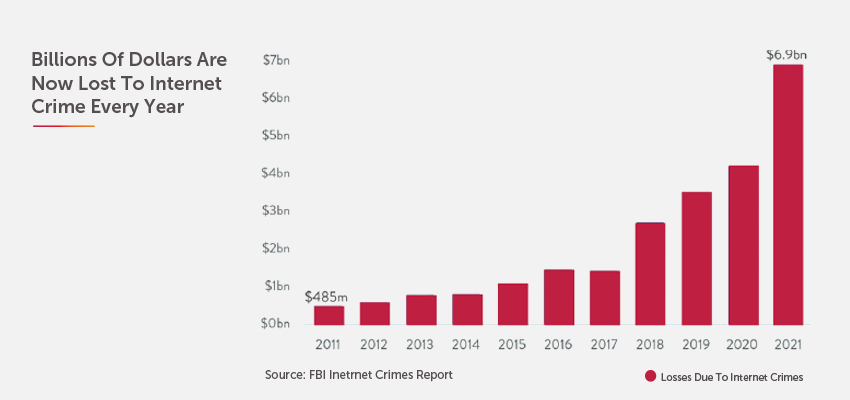
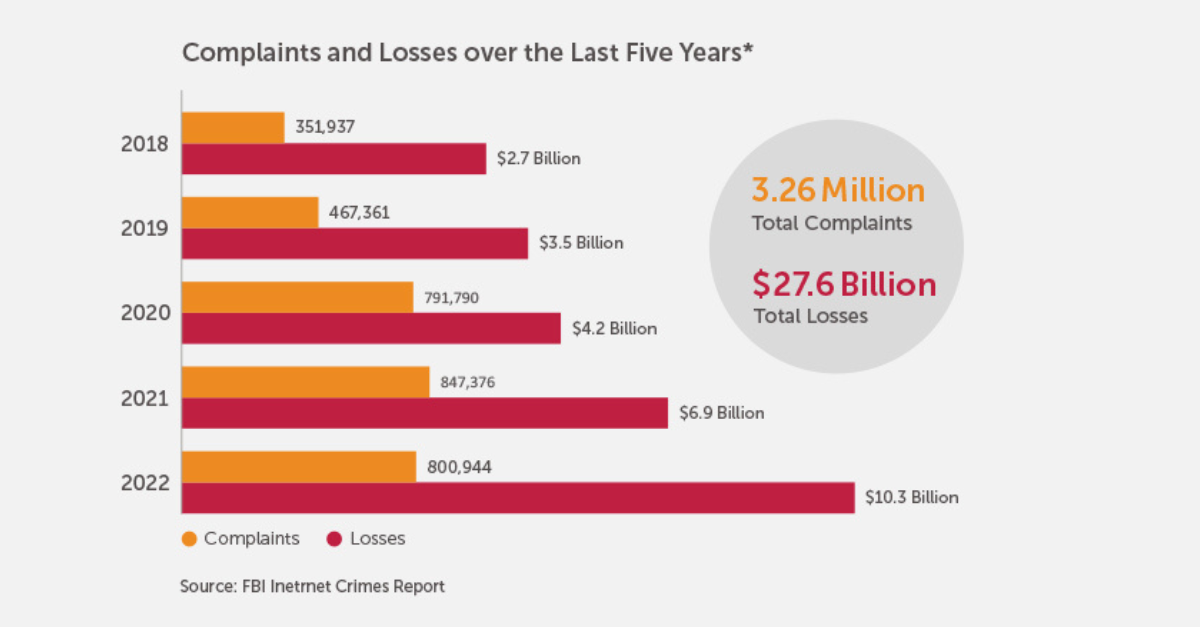
The power of the 5G network – high speed and throughput – also makes the network especially susceptible to cyber threats. Not only will higher customer usage make it more lucrative for hackers to increase their attacks, but the power of the network cloud will enable powerful web applications to be weaponized, at large scale, for even more sophisticated and powerful attacks. Every year we see a new record set in both the number of cybersecurity incidents and the overall socio-economic impact of cyber-attacks.
Also, the distributed nature of 5G networks creates new vulnerabilities for Bot and DDoS attacks in the network – turning the power of the network on itself. Attacks from connected devices will appear to emanate from the network and harm subscribers. This could seriously stress the network and harm CSP’s reputation. Having strong security at the CSP infrastructure core is not enough. Just like in a hub and spoke network, all nodes (i.e., consumer devices and MECs) need to be protected as well, since together they must form a secure network.
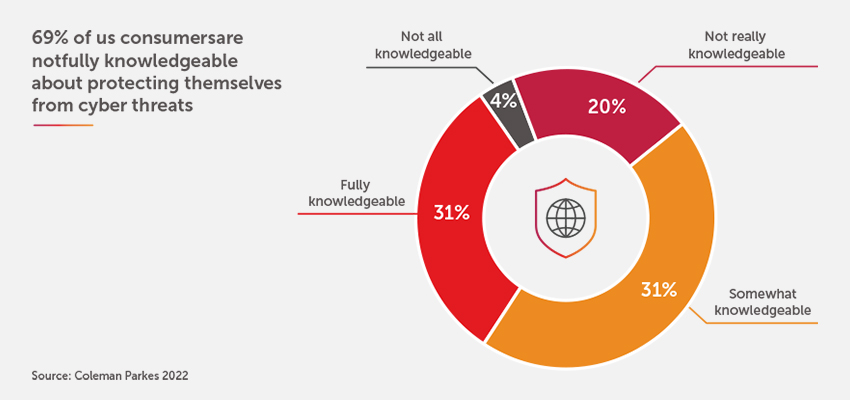
Lastly, to make this matter more challenging, surveys indicate that consumer awareness and knowledge about protecting themselves is quite low. There is a very low adoption of end-point security that consumers need to manage by themselves. What they need is a security solution that is pre-installed and pre-configured for them in the network itself, such that there is no need to deal with the hassle of downloading, managing, and maintaining a security application. The security solution should be native to the network!
Cyber-risks for 5G & how Network Native Security can protect consumers
With 5G, there is a significantly expanded attack surface due to several reasons:
- Massive numbers of low-security connected IoT devices.
- 100s of MECs (Mobile Edge Computing) with local breakouts are new targets for attacking the network.
- High speed and throughput of the network enabling more powerful and disruptive attacks.
App-based solutions (endpoint apps) are no longer adequate to support the rapid shift in consumer usage of 5G. While endpoint applications have their benefits in some use cases, they are no longer the industry benchmark that can provide cross-network security. Traditionally, less than 5% of consumers have downloaded security applications to their endpoint devices, due to lack of knowledge, time, or technical knowledge. Consumers cannot be expected to be their own tech support.
On the other hand, network native security can deliver a next-generation solution that is designed to scale with the growing adoption and evolution of 5G network security. By its very pre-installed and pre-configured nature, it provides zero-touch deployment with no maintenance requirements for the end user. CSPs can offer this core security to their customers from within the network itself, protecting them against malware and dangerous content, without impacting the resources of the mobile devices.
Allot Secure
The Allot Secure “Network Native” end-user protection components provide “single pane of glass” control and management to consumer and SMB customers, across all their devices, in both the mobile and home/business networks, including protecting them from internal network threats behind the router.
The Allot Secure network protection components offer scalable, containerized network-based security solutions, that are platform agnostic and are deployed to monitor the service provider’s 5G user plane to detect and mitigate both inbound and outbound DDoS attacks. The DDoS mitigation functionality uses network behavior anomaly detection, powered by machine learning algorithms, that even detects and blocks zero-day attacks.
In conclusion, 5G is not just a technology, it is a catalyst for change that will impact every aspect of our lives. CSPs have an opportunity to differentiate themselves through not just reliability and dependency, but also through network native consumer and network security. With the advent of 5G, we anticipate a dramatic change in how consumers will use fixed networks, and managing cyber-risks will be more important than ever before.
Listen to our podcast episode “5G Adoptation and the Role of Network Native Security” – Allot’s Product Marketing Director, Michael Schachter, discusses 5G adoptation in North America with Vikram Singh – Cybersecurity Marketing Director @ Allot.
FAQ
a. Unlimited data, faster speeds, and low latency enable new mobile applications and behaviors.
b. Explosion of machine-to-machine communication accelerates adoption of IoT devices and new services.
c. Consumers may primarily choose wireless networks over fixed networks for better experience and seamless connectivity.
a. High speed and throughput of 5G networks increase susceptibility to cyber threats.
b. The distributed nature of 5G networks creates vulnerabilities for Bot and DDoS attacks.
c. Low consumer awareness and adoption of endpoint security solutions further exacerbate cyber risks.
a. Massive numbers of low-security connected IoT devices expand attack surface.
b. Hundreds of Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) nodes become new targets for network attacks.
c. High speed and throughput enable more powerful and disruptive cyber attacks.
How can Network Native Security solutions address the cybersecurity challenges posed by 5G adoption?
a. Endpoint security solutions are inadequate due to low adoption rates and inability to provide cross-network security.
b. Network native security offers pre-installed and pre-configured protection within the network itself, scaling with 5G adoption.
c. Allot Secure provides network-based security solutions, including DDoS mitigation and malware protection, without impacting end users' devices.

 The importance of QoE for CSPs
The importance of QoE for CSPs What are the new cybersecurity trends every CSP should know?
What are the new cybersecurity trends every CSP should know? Mobile World Congress 2023 Wrap-up. 5G? Yes, but…
Mobile World Congress 2023 Wrap-up. 5G? Yes, but…